- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effects of Dietary Medlar ( Mespilus germanica L.) Extract on Growth Performance, Innate Immune Characteristics, Antioxidant Status, and Responses to Crowding Stress in Rainbow Trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Read this article at
Abstract
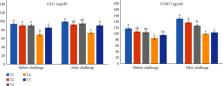
High stocking density is a stress factor that potentially affects physiological and immune responses. In this study, the effects of medlar ( Mespilus germanica) extract (ME) supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant, immune status, and stress responses in rainbow trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss) were studied. Six hundred fish (40.19 ± 1.09 g; average fish weight ± standard error) were distributed randomly into five experimental groups (assayed in triplicates). The experimental diets were formulated as follows: 0 (T1, control), 0.5% (T2), 1% (T3), 1.5% (T4), and 2% (T4). After 60 days feeding trial, the fish were confined, and the density increased (60 kg/m 3) for further 14 days. Results showed significant increases in final weight (FW), weight gain (WG), specific growth rate, and feed intake in the T4 compared to the control ( P < 0.05). The feed conversion ratio (FCR) in T4 significantly decreased compared to the control ( P < 0.05). Also, the treated groups showed significant improvements in catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), lysozyme (LYZ), total immunoglobulin (total Ig), respiratory burst activity (RBA), total protein, and phagocytosis (PHA) ( P < 0.05). Moreover, compared with the control group, supplementation could significantly decrease glucose (GLU) and cortisol (CORT), alanine transaminase (ALT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate transaminase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) ( P < 0.05). After the challenge, FW and WG in all treated challenge groups were significantly improved compared to the control group ( P < 0.05). FCR showed a significant decrease in all treated challenged groups compared to the control group ( P < 0.05). However, malondialdehyde, CAT, GPx, SOD, LYZ, complement activity (C3 and C4), total Ig, RBA, peroxidase, and PHA in challenged treated groups were significantly increased compared to the control group ( P < 0.05). All treated challenged groups showed lower ALT, LDH, AST, ALP, GLU, and CORT levels than the control group ( P < 0.05). The experiment herein successfully demonstrated that dietary ME stimulated fish growth, antioxidant status, and immune responses in crowding conditions and can be recommended as beneficial feed additives for rainbow trout.
Related collections
Most cited references92

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found