- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Cost‐Benefit Analysis of Government Compensation of Kidney Donors
Read this article at
Abstract
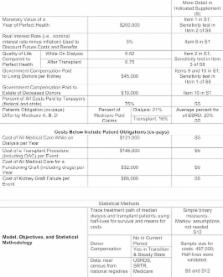
From 5000 to 10 000 kidney patients die prematurely in the United States each year, and about 100 000 more suffer the debilitating effects of dialysis, because of a shortage of transplant kidneys. To reduce this shortage, many advocate having the government compensate kidney donors. This paper presents a comprehensive cost‐benefit analysis of such a change. It considers not only the substantial savings to society because kidney recipients would no longer need expensive dialysis treatments—$1.45 million per kidney recipient—but also estimates the monetary value of the longer and healthier lives that kidney recipients enjoy—about $1.3 million per recipient. These numbers dwarf the proposed $45 000‐per‐kidney compensation that might be needed to end the kidney shortage and eliminate the kidney transplant waiting list. From the viewpoint of society, the net benefit from saving thousands of lives each year and reducing the suffering of 100 000 more receiving dialysis would be about $46 billion per year, with the benefits exceeding the costs by a factor of 3. In addition, it would save taxpayers about $12 billion each year.
Abstract
This analysis of a government program to compensate kidney donors indicates the monetary value of saving thousands of lives each year and reducing the suffering of a hundred thousand more on dialysis would be about $46 billion per year, and would save taxpayers about $12 billion a year.
Related collections
Most cited references13
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A study of the quality of life and cost-utility of renal transplantation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Effect of waiting time on renal transplant outcome.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found