- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Uncovering spatial and ecological variability in gap size frequency distributions in the Canadian boreal forest
Read this article at
Abstract
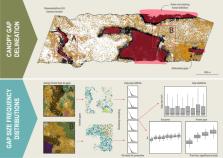
Analyses characterizing canopy gaps are required to improve our understanding of spatial and structural variations in forest canopies and provide insight into ecosystem-level successional processes. Gap size frequency distributions (GSFD) are indicative of ecological processes and disturbance patterns. To date, GSFD in boreal forest ecosystems have not been systematically quantified over large areas using a single consistent data source. Herein we characterized GSFDs across the entirety of the Canadian boreal forest using transects of airborne laser scanning (ALS) data. ALS transects were representatively sampled within eight distinct Canadian boreal ecozones. Gaps were detected and delineated from the ALS-derived canopy height model as contiguous canopy openings ≥8 m 2 with canopy heights ≤3 m. Gaps were then stratified by ecozone and forest type (i.e. coniferous, broadleaf, mixedwood, wetland-treed), and combinations thereof, and GSFDs were calculated for each stratum. GSFDs were characterized by the scaling parameter of the power-law probability distribution, lambda (λ) and Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests confirmed that GSFDs for each stratum followed a power-law distribution. Pairwise comparisons between ecozones, forest types, and combinations thereof indicated significant differences between estimates of λ. Scaling parameters were found to be more variable by ecozone (1.96–2.31) than by forest type (2.15–2.21). These results contrast those of similar studies done in tropical forest environments, whereby λ was found to be relatively consistent across a range of site types, geological substrates, and forest types. The geographic range considered herein is much larger than that of previous studies, and broad-scale patterns in climate, landforms, and soils that are reflected in the definition of unique ecozones, likely also influence gap characteristics.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fire in the Earth system.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Gap-Phase Regeneration in a Tropical Forest
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found