- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Covid-19 pandemic in context of climate change perception and resource-saving behavior in the European Union countries
Read this article at
Abstract
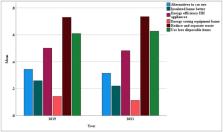
The resource-saving behavior in the recent period is escalating particularly due to the energy and prices crises in all of the European Union (EU). The COVID-19 pandemic not only caused changes in health concerns but also in environmental awareness and behavior. Thus, this paper aims to reveal whether the COVID-19 pandemic contributed to the resource-saving behavior, and how this pandemic changed the climate change perception and personal responsibility in the EU countries. Referring to two surveys conducted in all EU countries in 2019 and 2021, the results revealed that the level of climate change perception during this period significantly decreased in all EU. Meanwhile, the level of responsibility placed on the government to solve the climate change problem increased the most. A level of the personal responsibility increased negligibly. Considering resource-saving behaviors, only the lesser usage of disposable items from 2019 to 2021 increased statistically significantly. The results of an analysis of the main determinants of resource-saving behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic period revealed that personal responsibility and the climate change solution's benefit for health positively and significantly determined all the analyzed actions. The climate change perception and climate change solution's benefit for the economy statistically significantly influenced waste reduction, the purchase of efficient appliances, and the usage of pro-environmental transportation mode instead of personal cars. Health benefits instead of the economic benefits statistically significantly contributed to the resource-saving behaviors, except for actions that require more monetary investments. The satisfaction with the COVID-19 pandemic management had an insignificant negative impact on all resource-saving actions. Thus, the tools assigned to manage this pandemic did not motivate people to save natural resources.
Related collections
Most cited references74
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The psychological impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on college students in China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
