- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
REAPR: a universal tool for genome assembly evaluation
Read this article at
Abstract
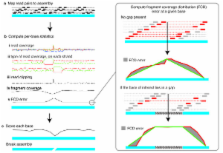
Methods to reliably assess the accuracy of genome sequence data are lacking. Currently completeness is only described qualitatively and mis-assemblies are overlooked. Here we present REAPR, a tool that precisely identifies errors in genome assemblies without the need for a reference sequence. We have validated REAPR on complete genomes or de novo assemblies from bacteria, malaria and Caenorhabditis elegans, and demonstrate that 86% and 82% of the human and mouse reference genomes are error-free, respectively. When applied to an ongoing genome project, REAPR provides corrected assembly statistics allowing the quantitative comparison of multiple assemblies. REAPR is available at http://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/software/reapr/.
Related collections
Most cited references18

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Toward almost closed genomes with GapFiller
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
SSAHA: a fast search method for large DNA databases.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found