- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Feasibility, acceptability and preliminary evaluation of a user co-facilitated psychoeducational programme: a feasibility proof-of-concept randomised control trial
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Mental health settings are increasingly using co-facilitation of educational group interventions in collaboration with patient partners and service users. However, despite promising results, limited information is available regarding the feasibility and satisfaction levels of these programmes among adults newly diagnosed with attention-deficit hyperactivity/impulsivity disorder (ADHD). Hence, this study aimed to determine the feasibility, acceptability, and preliminary effects of a user co-facilitated psychoeducational group programme for adults diagnosed with ADHD.
Methods
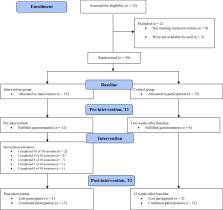
This feasibility proof-of-concept randomised controlled trial recruited outpatients from a Norwegian community mental health centre. Outpatients randomised to the intervention group (IG) received a psychoeducational programme supplementing Treatment As Usual (TAU), while the control group received TAU. Feasibility was determined by the acceptance rate, adherence rate, and dropout rate. Acceptability was measured with the Client Satisfaction Questionnaire and a 3-item scale measuring satisfaction with the received information. To test the preliminary effects, self-efficacy, symptom severity, and quality of life were measured at baseline and pre- and post-intervention.
Results
Feasibility was demonstrated; most of the patients were willing to enrol, participants attended 82% of the psychoeducational programme, and only 13% dropped out of the study. The between-group analyses revealed that the IG reported significantly greater mean satisfaction than the CG. Moreover, the intervention group was more satisfied with the information they received during the psychoeducational programme. Concerning the preliminary effects, the linear mixed model showed improvement in quality of life (the subscale relationship); however, other patient-reported outcomes did not show improvements.
Conclusions
This proof-of-concept randomised controlled trial supports the feasibility and acceptability of the user co-facilitated psychoeducational programme for patients newly diagnosed with ADHD in an outpatient setting. While preliminary findings indicate promise in enhancing patient-reported outcomes, a larger study is warranted to assess the intervention’s effectiveness rigorously.
Related collections
Most cited references79

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Acceptability of healthcare interventions: an overview of reviews and development of a theoretical framework

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
CONSORT 2010 Statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.