- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Dissecting the Dual Nature of Hyaluronan in the Tumor Microenvironment
Read this article at
Abstract
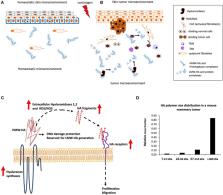
Hyaluronan (HA) is a glycosaminoglycan with a simple structure but diverse and often opposing functions. The biological activities of this polysaccharide depend on its molecular weight and the identity of interacting receptors. HA is initially synthesized as high molecular-weight (HMW) polymers, which maintain homeostasis and restrain cell proliferation and migration in normal tissues. These HMW-HA functions are mediated by constitutively expressed receptors including CD44, LYVE-1, and STABILIN2. During normal processes such as tissue remodeling and wound healing, HMW-HA is fragmented into low molecular weight polymers (LMW-HA) by hyaluronidases and free radicals, which promote inflammation, immune cell recruitment and the epithelial cell migration. These functions are mediated by RHAMM and TLR2,4, which coordinate signaling with CD44 and other HA receptors. Tumor cells hijack the normally tightly regulated HA production/fragmentation associated with wound repair/remodeling, and these HA functions participate in driving and maintaining malignant progression. However, elevated HMW-HA production in the absence of fragmentation is linked to cancer resistance. The controlled production of HA polymer sizes and their functions are predicted to be key to dissecting the role of microenvironment in permitting or restraining the oncogenic potential of tissues. This review focuses on the dual nature of HA in cancer initiation vs. resistance, and the therapeutic potential of HA for chemo-prevention and as a target for cancer management.
Related collections
Most cited references92

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Interactions between Hyaluronan and Its Receptors (CD44, RHAMM) Regulate the Activities of Inflammation and Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found