- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Applying a brain-computer interface to support motor imagery practice in people with stroke for upper limb recovery: a feasibility study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
There is now sufficient evidence that using a rehabilitation protocol involving motor imagery (MI) practice in conjunction with physical practice (PP) of goal-directed rehabilitation tasks leads to enhanced functional recovery of paralyzed limbs among stroke sufferers. It is however difficult to confirm patient engagement during an MI in the absence of any on-line measure. Fortunately an EEG-based brain-computer interface (BCI) can provide an on-line measure of MI activity as a neurofeedback for the BCI user to help him/her focus better on the MI task. However initial performance of novice BCI users may be quite moderate and may cause frustration. This paper reports a pilot study in which a BCI system is used to provide a computer game-based neurofeedback to stroke participants during the MI part of a protocol.
Methods
The participants included five chronic hemiplegic stroke sufferers. Participants received up to twelve 30-minute MI practice sessions (in conjunction with PP sessions of the same duration) on 2 days a week for 6 weeks. The BCI neurofeedback performance was evaluated based on the MI task classification accuracy (CA) rate. A set of outcome measures including action research arm test (ARAT) and grip strength (GS), was made use of in assessing the upper limb functional recovery. In addition, since stroke sufferers often experience physical tiredness, which may influence the protocol effectiveness, their fatigue and mood levels were assessed regularly.
Results
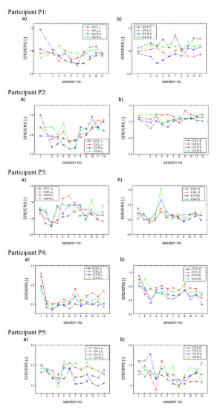
Positive improvement in at least one of the outcome measures was observed in all the participants, while improvements approached a minimal clinically important difference (MCID) for the ARAT. The on-line CA of MI induced sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) modulation patterns in the form of lateralized event-related desynchronization (ERD) and event-related synchronization (ERS) effects, for novice participants was in a moderate range of 60-75% within the limited 12 training sessions. The ERD/ERS change from the first to the last session was statistically significant for only two participants.
Conclusions
Overall the crucial observation is that the moderate BCI classification performance did not impede the positive rehabilitation trends as quantified with the rehabilitation outcome measures adopted in this study. Therefore it can be concluded that the BCI supported MI is a feasible intervention as part of a post-stroke rehabilitation protocol combining both PP and MI practice of rehabilitation tasks. Although these findings are promising, the scope of the final conclusions is limited by the small sample size and the lack of a control group.
Related collections
Most cited references16
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
A performance test for assessment of upper limb function in physical rehabilitation treatment and research.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The assessment of fatigue: a practical guide for clinicians and researchers.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found