- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Enhanced photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic behaviors of MFe 2O 4 (M = Ni, Co, Zn and Sr) modified TiO 2 nanorod arrays
Read this article at
Abstract
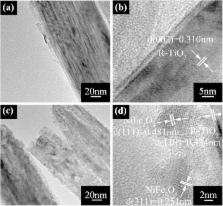
Modified TiO 2 nanomaterials are considered to be promising in energy conversion and ferrites modification may be one of the most efficient modifications. In this research, various ferrites, incorporated with various cations (MFe 2O 4, M = Ni, Co, Zn, and Sr), are utilized to modify the well aligned TiO 2 nanorod arrays (NRAs), which is synthesized by hydrothermal method. It is found that all MFe 2O 4/TiO 2 NRAs show obvious red shift into the visible light region compared with the TiO 2 NRAs. In particular, NiFe 2O 4 modification is demonstrated to be the best way to enhance the photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic activity of TiO 2 NRAs. Furthermore, the separation and transfer of charge carriers after MFe 2O 4 modification are clarified by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements. Finally, the underlying mechanism accounting for the enhanced photocatalytic activity of MFe 2O 4/TiO 2 NRAs is proposed. Through comparison among different transition metals modified TiO 2 with the same synthesis process and under the same evaluating condition, this work may provide new insight in designing modified TiO 2 nanomaterials as visible light active photocatalysts.
Related collections
Most cited references12
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Ni(x)Co(3-x)O(4) nanowire arrays for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comparing graphene-TiO₂ nanowire and graphene-TiO₂ nanoparticle composite photocatalysts.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found