- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Streptococcus pneumoniae’s Virulence and Host Immunity: Aging, Diagnostics, and Prevention
Read this article at
Abstract
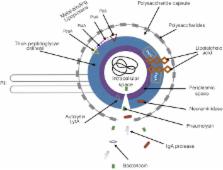
Streptococcus pneumoniae is an infectious pathogen responsible for millions of deaths worldwide. Diseases caused by this bacterium are classified as pneumococcal diseases. This pathogen colonizes the nasopharynx of its host asymptomatically, but overtime can migrate to sterile tissues and organs and cause infections. Pneumonia is currently the most common pneumococcal disease. Pneumococcal pneumonia is a global health concern and vastly affects children under the age of five as well as the elderly and individuals with pre-existing health conditions. S. pneumoniae has a large selection of virulence factors that promote adherence, invasion of host tissues, and allows it to escape host immune defenses. A clear understanding of S. pneumoniae’s virulence factors, host immune responses, and examining the current techniques available for diagnosis, treatment, and disease prevention will allow for better regulation of the pathogen and its diseases. In terms of disease prevention, other considerations must include the effects of age on responses to vaccines and vaccine efficacy. Ongoing work aims to improve on current vaccination paradigms by including the use of serotype-independent vaccines, such as protein and whole cell vaccines. Extending our knowledge of the biology of, and associated host immune response to S. pneumoniae is paramount for our improvement of pneumococcal disease diagnosis, treatment, and improvement of patient outlook.
Related collections
Most cited references272
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nod2 is a general sensor of peptidoglycan through muramyl dipeptide (MDP) detection.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Infants and Children Older Than 3 Months of Age: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found