- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Defected ZnWO 4-decorated WO 3 nanorod arrays for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting†
Read this article at
Abstract
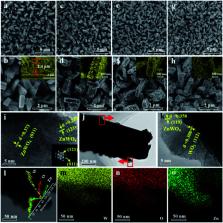
The utilization of solar energy in photoelectrochemical water splitting is a popular approach to store solar energy and minimize the dependence on fossil fuels. Herein, defected ZnWO 4-decorated WO 3 nanorod arrays with type II heterojunction structures were synthesized via a two-step solvothermal method. By controlling the amount of Zn precursor, WO 3 nanorods were decorated in situ with tunable amounts of ZnWO 4 nanoparticles. Characterization confirmed the presence of abundant W 5+ species in the defected ZnWO 4-decorated WO 3 samples, leading to enhanced light absorption and charge-separation efficiency. Therefore, the decorated WO 3 nanorod arrays show much higher photoelectrochemical (PEC) activity than pure WO 3 nanorod arrays. Specifically, the sample with optimal ZnWO 4 decoration and surface defects exhibits a current density of 1.87 mA cm −2 in water splitting at 1.23 V vs. RHE under 1 sun irradiation (almost 2.36 times higher than that of pure WO 3), a high incident photon-to-current efficiency of nearly 40% at 350 nm, and a relatively high photostability. However, the decoration of WO 3 with too much ZnWO 4 blocks the light absorption of WO 3, inhibiting the PEC performance, even when many defects are present. This work provides a promising approach to rationally construct defected heterojunctions as highly active PEC anodes for practical applications.
Abstract
A strategy based on a solvothermal method was developed to construct defected ZnWO 4-decorated WO 3 photoanodes for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting.
