- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Anti-inflammatory Effects of Perioperative Dexmedetomidine Administered as an Adjunct to General Anesthesia: A Meta-analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
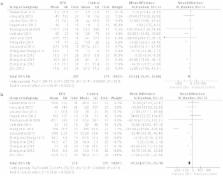
The aim of this meta-analysis is to examine the effects of dexmedetomidine on serum inflammatory markers when administered perioperatively. We searched multiple electronic databases for relevant research papers, and carried out meta-analyses of weighted mean differences and interpreted in the light of statistical heterogeneity (I 2). Fifteen RCTs recruiting 641 patients were included. Dexmedetomidine treatment significantly decreased interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) levels with mean differences [95% CI] in the changes from baseline between dexmedetomidine treated and controls of −25.14 [−35.29, −15.00]; P < 0.00001 (for IL-6), −5.69 [−10.77, −0.60]; P < 0.04 (for IL-8), and −20.30 [−30.93, −9.67]; P < 0.0002 (for TNF-α) immediately after surgery; and −41.55 [−57.41, −25.70]; P < 0.00001 (IL-6), −6.46 [−10.83, −2.08]; P < 0.005 (IL-8), and −14.67 [−22.61, −6.73]; P < 0.0003 (TNF-α) on postoperative day 1 (random effects). IL-10 levels were found to increase significantly a day after surgery (8.33 [3.31, 13.36]; P = 0.001). Subgroup analyses did not reveal significant differences. In conclusion, perioperative adjunctive use of dexmedetomidine substantially decreases serum IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α levels.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Inflammation in wound repair: molecular and cellular mechanisms.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha: A Link between Neuroinflammation and Excitotoxicity
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found