- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Development and exploitation of a novel mutant androgen receptor modelling strategy to identify new targets for advanced prostate cancer therapy
Read this article at
Abstract
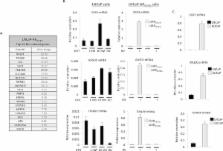
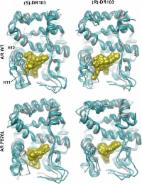
The persistence of androgen receptor (AR) signalling in castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) highlights the unmet clinical need for the development of more effective AR targeting therapies. A key mechanism of therapy-resistance is by selection of AR mutations that convert anti-androgens to agonists enabling the retention of androgenic signalling in CRPC. To improve our understanding of these receptors in advanced disease we developed a physiologically-relevant model to analyse the global functionality of AR mutants in CRPC. Using the bicalutamide-activated AR W741L/C mutation as proof of concept, we demonstrate that this mutant confers an androgenic-like signalling programme and growth promoting phenotype in the presence of bicalutamide. Transcriptomic profiling of AR W741L highlighted key genes markedly up-regulated by the mutant receptor, including TIPARP, RASD1 and SGK1. Importantly, SGK1 expression was found to be highly expressed in the KUCaP xenograft model and a CRPC patient biopsy sample both of which express the bicalutamide-activated receptor mutant. Using an SGK1 inhibitor, AR W741L transcriptional and growth promoting activity was reduced indicating that exploiting functional distinctions between receptor isoforms in our model may provide new and effective therapies for CRPC patients.
Related collections
Most cited references23
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gene expression signature-based chemical genomic prediction identifies a novel class of HSP90 pathway modulators.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found