- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Target identification of natural medicine with chemical proteomics approach: probe synthesis, target fishing and protein identification
Read this article at
Abstract
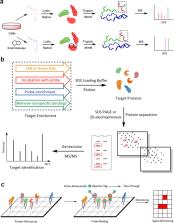
Natural products are an important source of new drugs for the treatment of various diseases. However, developing natural product-based new medicines through random moiety modification is a lengthy and costly process, due in part to the difficulties associated with comprehensively understanding the mechanism of action and the side effects. Identifying the protein targets of natural products is an effective strategy, but most medicines interact with multiple protein targets, which complicate this process. In recent years, an increasing number of researchers have begun to screen the target proteins of natural products with chemical proteomics approaches, which can provide a more comprehensive array of the protein targets of active small molecules in an unbiased manner. Typically, chemical proteomics experiments for target identification consist of two key steps: (1) chemical probe design and synthesis and (2) target fishing and identification. In recent decades, five different types of chemical proteomic probes and their respective target fishing methods have been developed to screen targets of molecules with different structures, and a variety of protein identification approaches have been invented. Presently, we will classify these chemical proteomics approaches, the application scopes and characteristics of the different types of chemical probes, the different protein identification methods, and the advantages and disadvantages of these strategies.
Related collections
Most cited references126
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The cellular thermal shift assay for evaluating drug target interactions in cells.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found