- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Recovery From Severe Mental Health Problems: A Systematic Review of Service User and Informal Caregiver Perspectives
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction: The recovery approach aims to have users' perspectives at the heart of service development and research; it is a holistic perspective that considers social needs, personal growth and inclusion. In the last decade recovery-oriented research and practice has increased greatly, however, a comprehensive model of recovery considering exclusively the perspectives of people with lived experience has not been devised.
Aims: This review aimed to develop a framework and contextualize service users' and informal caregivers' understanding of recovery from severe mental health problems.
Methods: We systematically searched 6 databases including key terms related to knowledge, experience and narratives AND mental health AND personal recovery. The search was supplemented with reference sourcing through gray literature, reference tracking and expert consultation. Data analysis consisted of a qualitative meta-synthesis using constant comparative methods.
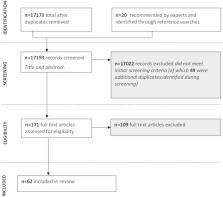
Results: Sixty-two studies were analyzed. A pattern emerged regarding the recovery paradigms that the studies used to frame their findings. The resulting recovery framework included the domains Social recovery; Prosperity (Legal, political, and economic recovery); Individual Recovery; and Clinical Recovery Experience (SPICE). Service users' definitions of recovery tended to prioritize social aspects, particularly being accepted and connecting with others, while caregivers focused instead on clinical definitions of recovery such as symptom remission. Both groups emphasized individual aspects such as becoming self-sufficient and achieving personal goals, which was strongly linked with having economic means for independence.
Conclusions: The recovery model provided by this review offers a template for further research in the field and a guide for policy and practice. Predominant definitions of recovery currently reflect understandings of mental health which focus on an individual perspective, while this review found an important emphasis on socio-political aspects. At the same time, only a small number of studies took place in low-income countries, focused on minoritized populations, or included caregivers' perspectives. These are important gaps in the literature that require further attention.
Systematic Review Registration: The review protocol was registered on PROSPERO (CRD42017076450); https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=76450.
Related collections
Most cited references119
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found