- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Evaluation of the prognostic role of centromere 17 gain and HER2/topoisomerase II alpha gene status and protein expression in patients with breast cancer treated with anthracycline-containing adjuvant chemotherapy: pooled analysis of two Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) phase III trials

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The HER2 gene has been established as a valid biological marker for the treatment of breast cancer patients with trastuzumab and probably other agents, such as paclitaxel and anthracyclines. The TOP2A gene has been associated with response to anthracyclines. Limited information exists on the relationship of HER2/ TOP2A gene status in the presence of centromere 17 (CEP17) gain with outcome of patients treated with anthracycline-containing adjuvant chemotherapy.
Methods
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor tissue samples from 1031 patients with high-risk operable breast cancer, enrolled in two consecutive phase III trials, were assessed in a central laboratory by fluorescence in situ hybridization for HER2/ TOP2A gene amplification and CEP17 gain (CEP17 probe). Amplification of HER2 and TOP2A were defined as a gene/CEP17 ratio of >2.2 and ≥2.0, respectively, or gene copy number higher than 6. Additionally, HER2, TopoIIa, ER/PgR and Ki67 protein expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and patients were classified according to their IHC phenotype. Treatment consisted of epirubicin-based adjuvant chemotherapy followed by hormonal therapy and radiation, as indicated.
Results
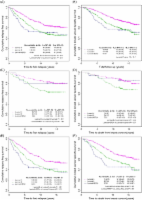
HER2 amplification was found in 23.7% of the patients and TOP2A amplification in 10.1%. In total, 41.8% of HER2-amplified tumors demonstrated TOP2A co-amplification. The median (range) of HER2, TOP2A and CEP17 gain was 2.55 (0.70-45.15), 2.20 (0.70-26.15) and 2.00 (0.70-26.55), respectively. Forty percent of the tumors had CEP17 gain (51% of those with HER2 amplification). Adjusting for treatment groups in the Cox model, HER2 amplification, TOP2A amplification, CEP17 gain and HER2/ TOP2A co-amplification were not associated with time to relapse or time to death.
Conclusion
HER2 amplification, TOP2A amplification, CEP17 gain and HER2/ TOP2A co-amplification were not associated with outcome in high-risk breast cancer patients treated with anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy.
Trial registration
Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ANZCTR) ACTRN12611000506998 and ACTRN12609001036202
Related collections
Most cited references64
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ki67 Index, HER2 Status, and Prognosis of Patients With Luminal B Breast Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK).
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.