- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Read this article at
Abstract
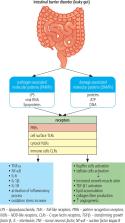
The gut microbiota has recently been recognized as a major environmental factor in the pathophysiology of several human diseases. The anatomical and functional association existing between the gut and the liver provides the theoretical basis to assume that the liver is a major target for gut microbes. In the last decades, many studies have reported an altered composition of gut microbiota in patients with chronic liver diseases and liver cirrhosis, suggesting a progressively marked dysbiosis to be related to worsening of the liver disease. Modifications of microbiota result in alteration in providing signals through the intestine and bacterial products, as well as hormones produced in the bowel that affect metabolism at different levels including the liver. There is increasing evidence for a correlation between intestinal microbiota, bacterial translocation and hepatic steatosis. Intestinal microbiota affects nutrient absorption and energy homeostasis. Altered intestinal permeability may favor the passage of bacteria derived compounds into the systemic circulation, causing a systemic inflammatory state, characteristic of the metabolic syndrome. At present, an increasing number of studies indicate a close relationship between dysbiosis, defined as abnormal composition and the amount of intestinal bacteria (gut microbiota), intestinal permeability and some metabolic, inflammatory, degenerative and even psychiatric diseases. Microbiota pharmacological modulation seems to be a promising tool for a new therapeutic approach to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and in prevention of cirrhosis.
The following study aims to briefly discuss the role of microbiota disorder (dysbiosis), and in particular small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Related collections
Most cited references41
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A multicenter prospective study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Bifidobacterium longum with fructo-oligosaccharides in patients with non alcoholic steatohepatitis.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found