- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Applications of Alginate-Based Nanomaterials in Enhancing the Therapeutic Effects of Bee Products
Read this article at
Abstract
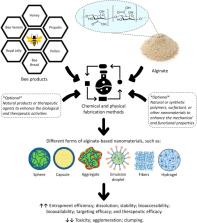
Since the ancient times, bee products (i.e., honey, propolis, pollen, bee venom, bee bread, and royal jelly) have been considered as natural remedies with therapeutic effects against a number of diseases. The therapeutic pleiotropy of bee products is due to their diverse composition and chemical properties, which is independent on the bee species. This has encouraged researchers to extensively study the therapeutic potentials of these products, especially honey. On the other hand, amid the unprecedented growth in nanotechnology research and applications, nanomaterials with various characteristics have been utilized to improve the therapeutic efficiency of these products. Towards keeping the bee products as natural and non-toxic therapeutics, the green synthesis of nanocarriers loaded with these products or their extracts has received a special attention. Alginate is a naturally produced biopolymer derived from brown algae, the desirable properties of which include biodegradability, biocompatibility, non-toxicity and non-immunogenicity. This review presents an overview of alginates, including their properties, nanoformulations, and pharmaceutical applications, placing a particular emphasis on their applications for the enhancement of the therapeutic effects of bee products. Despite the paucity of studies on fabrication of alginate-based nanomaterials loaded with bee products or their extracts, recent advances in the area of utilizing alginate-based nanomaterials and other types of materials to enhance the therapeutic potentials of bee products are summarized in this work. As the most widespread and well-studied bee products, honey and propolis have garnered a special interest; combining them with alginate-based nanomaterials has led to promising findings, especially for wound healing and skin tissue engineering. Furthermore, future directions are proposed and discussed to encourage researchers to develop alginate-based stingless bee product nanomedicines, and to help in selecting suitable methods for devising nanoformulations based on multi-criteria decision making models. Also, the commercialization prospects of nanocomposites based on alginates and bee products are discussed. In conclusion, preserving original characteristics of the bee products is a critical challenge in developing nano-carrier systems. Alginate-based nanomaterials are well suited for this task because they can be fabricated without the use of harsh conditions, such as shear force and freeze-drying, which are often used for other nano-carriers. Further, conjunction of alginates with natural polymers such as honey does not only combine the medicinal properties of alginates and honey, but it could also enhance the mechanical properties and cell adhesion capacity of alginates.
Related collections
Most cited references276

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Alginate: properties and biomedical applications.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found