- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The promise of layer-specific neuroimaging for testing predictive coding theories of psychosis
Read this article at
Abstract
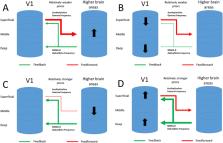
Predictive coding potentially provides an explanatory model for understanding the neurocognitive mechanisms of psychosis. It proposes that cognitive processes, such as perception and inference, are implemented by a hierarchical system, with the influence of each level being a function of the estimated precision of beliefs at that level. However, predictive coding models of psychosis are insufficiently constrained—any phenomenon can be explained in multiple ways by postulating different changes to precision at different levels of processing. One reason for the lack of constraint in these models is that the core processes are thought to be implemented by the function of specific cortical layers, and the technology to measure layer specific neural activity in humans has until recently been lacking. As a result, our ability to constrain the models with empirical data has been limited. In this review we provide a brief overview of predictive processing models of psychosis and then describe the potential for newly developed, layer specific neuroimaging techniques to test and thus constrain these models. We conclude by discussing the most promising avenues for this research as well as the technical and conceptual challenges which may limit its application.
Related collections
Most cited references111
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The free-energy principle: a unified brain theory?
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Predictive coding in the visual cortex: a functional interpretation of some extra-classical receptive-field effects.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found