- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Induction of Autophagy to Achieve a Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Cure
Read this article at
Abstract
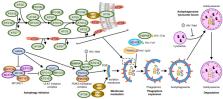
Effective antiretroviral therapy has led to significant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) suppression and improvement in immune function. However, the persistence of integrated proviral DNA in latently infected reservoir cells, which drive viral rebound post-interruption of antiretroviral therapy, remains the major roadblock to a cure. Therefore, the targeted elimination or permanent silencing of this latently infected reservoir is a major focus of HIV-1 research. The most studied approach in the development of a cure is the activation of HIV-1 expression to expose latently infected cells for immune clearance while inducing HIV-1 cytotoxicity—the “kick and kill” approach. However, the complex and highly heterogeneous nature of the latent reservoir, combined with the failure of clinical trials to reduce the reservoir size casts doubt on the feasibility of this approach. This concern that total elimination of HIV-1 from the body may not be possible has led to increased emphasis on a “functional cure” where the virus remains but is unable to reactivate which presents the challenge of permanently silencing transcription of HIV-1 for prolonged drug-free remission—a “block and lock” approach. In this review, we discuss the interaction of HIV-1 and autophagy, and the exploitation of autophagy to kill selectively HIV-1 latently infected cells as part of a cure strategy. The cure strategy proposed has the advantage of significantly decreasing the size of the HIV-1 reservoir that can contribute to a functional cure and when optimised has the potential to eradicate completely HIV-1.
Related collections
Most cited references235
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found