- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Plant-level intensity of energy and CO 2 emissions for Portland cement in Guizhou of Southwest China 2019–2022
Read this article at
Abstract
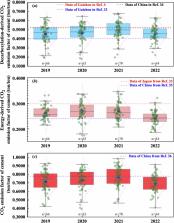
Low-carbon development of ordinary Portland cement industry is of great significance to China’s target “to peak carbon dioxide emissions before 2030 and to achieve carbon neutrality before 2060”. Neglecting the regional heterogeneity in China, few studies emphasized the status and developments of energy intensity and CO 2 emissions of ordinary Portland cement industry in Guizhou of Southwest China. To bridge this knowledge gap, we present an annual intensity dataset of energy and CO 2 emissions at plant-level for Guizhou’s ordinary Portland cement industry, which involves the details of clinker rotary kilns, yearly production of clinker and cement products, fuel consumption and electricity consumption, total CO 2 emission of cement products, energy intensity indicators of clinker and cement products, utilization ratio of solid-waste in clinker and cement production, and CO 2 emission factors of cement products. It is an important supplement and to existing energy intensity and CO 2 emissions estimates at plant-level and provincial official emissions inventories that converges all regions of China.
Related collections
Most cited references30

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Carbon Monitor, a near-real-time daily dataset of global CO 2 emission from fossil fuel and cement production
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The Durability of Alkali-Activated Materials in Comparison with Ordinary Portland Cements and Concretes: A Review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found