- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Closing Yield Gaps: How Sustainable Can We Be?

Read this article at
Abstract
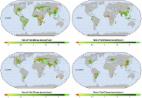
Global food production needs to be increased by 60–110% between 2005 and 2050 to meet growing food and feed demand. Intensification and/or expansion of agriculture are the two main options available to meet the growing crop demands. Land conversion to expand cultivated land increases GHG emissions and impacts biodiversity and ecosystem services. Closing yield gaps to attain potential yields may be a viable option to increase the global crop production. Traditional methods of agricultural intensification often have negative externalities. Therefore, there is a need to explore location-specific methods of sustainable agricultural intensification. We identified regions where the achievement of potential crop calorie production on currently cultivated land will meet the present and future food demand based on scenario analyses considering population growth and changes in dietary habits. By closing yield gaps in the current irrigated and rain-fed cultivated land, about 24% and 80% more crop calories can respectively be produced compared to 2000. Most countries will reach food self-sufficiency or improve their current food self-sufficiency levels if potential crop production levels are achieved. As a novel approach, we defined specific input and agricultural management strategies required to achieve the potential production by overcoming biophysical and socioeconomic constraints causing yield gaps. The management strategies include: fertilizers, pesticides, advanced soil management, land improvement, management strategies coping with weather induced yield variability, and improving market accessibility. Finally, we estimated the required fertilizers (N, P 2O 5, and K 2O) to attain the potential yields. Globally, N-fertilizer application needs to increase by 45–73%, P 2O 5-fertilizer by 22–46%, and K 2O-fertilizer by 2–3 times compared to the year 2010 to attain potential crop production. The sustainability of such agricultural intensification largely depends on the way management strategies for closing yield gaps are chosen and implemented.
Related collections
Most cited references8
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Yield Trends Are Insufficient to Double Global Crop Production by 2050
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The impact of climate change on smallholder and subsistence agriculture.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found