- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Emerging roles and the regulation of aerobic glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Read this article at
Abstract
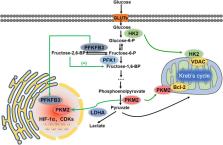
Liver cancer has become the sixth most diagnosed cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is responsible for up to 75–85% of primary liver cancers, and sorafenib is the first targeted drug for advanced HCC treatment. However, sorafenib resistance is common because of the resultant enhancement of aerobic glycolysis and other molecular mechanisms. Aerobic glycolysis was firstly found in HCC, acts as a hallmark of liver cancer and is responsible for the regulation of proliferation, immune evasion, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and drug resistance in HCC. The three rate-limiting enzymes in the glycolytic pathway, including hexokinase 2 (HK2), phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK1), and pyruvate kinases type M2 (PKM2) play an important role in the regulation of aerobic glycolysis in HCC and can be regulated by many mechanisms, such as the AMPK, PI3K/Akt pathway, HIF-1α, c-Myc and noncoding RNAs. Because of the importance of aerobic glycolysis in the progression of HCC, targeting key factors in its pathway such as the inhibition of HK2, PFK or PKM2, represent potential new therapeutic approaches for the treatment of HCC.
Related collections
Most cited references149
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pyruvate kinase M2 is a PHD3-stimulated coactivator for hypoxia-inducible factor 1.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found