- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Should Virtual Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) Teaching Replace or Complement Face-to-Face Teaching in the Post-COVID-19 Educational Environment: An Evaluation of an Innovative National COVID-19 Teaching Programme
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The COVID-19 pandemic brought about drastic changes to medical education and examinations, with a shift to online lectures and webinars. Additionally, social restrictions in the United Kingdom (UK) inhibited students’ ability to practice for objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) with their peers.
Methods
The Virtual OSCE buddy scheme (VOBS) provided a means to practice OSCE skills virtually by linking groups of 2-6 final-year medical students with a junior doctor who had recently passed their exams. Sessions were held virtually, tailored to the needs of each group, in a 3-month period prior to examinations. The scheme ran across two examination periods, 2020/21 and 2021/22, including a total of 13 universities throughout the UK.
Results
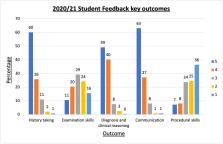
In 2020/21, 96% (n=227) of students described improved confidence in OSCE scenarios. Furthermore, 90% (n=213) reported improvement in communication, 89% (n=211) in diagnosis and clinical reasoning and 86% (n=203) in history-taking skills. Examination and procedural skills proved more challenging to practice virtually, with improvement reported by 31% (n=73) and 15% (n=36) of students, respectively. Ninety-three per cent (n=58) of buddies reported improved lesson planning abilities and 90% (n=57) felt more confident in their teaching.
In 2021/22, 90% (n=133) of students felt more prepared for their OSCE. In key skills, improvement was reported by 87% (n=128) in communication, 84% (n=124) in diagnosis and clinical reasoning and 83% (n=123) in history-taking. In this cohort, 40% (n=59) reported improvement in examination skills and 24% (n=36) in procedural skills. Ninety per cent (n=83) of buddies reported an improvement in teaching skills, with 93% (n=85) increasing their confidence to teach.
Conclusion
VOBS demonstrates the benefits to students and teachers of near-peer OSCE teaching. Given the virtual nature, the main drawback is the inability to practice hands-on examination and procedural skills. This scheme provides insight to educators planning virtual teaching programmes in the future. With the evolution of technology, virtual examination and procedure practice may be possible in the near future. VOBS would suggest that currently, virtual OSCE teaching should be used to complement face-to-face teaching.
Related collections
Most cited references19

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Perceptions of medical students towards online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic: a national cross-sectional survey of 2721 UK medical students
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on final year medical students in the United Kingdom: a national survey
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found