- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Differential microglia and macrophage profiles in human IDH-mutant and -wild type glioblastoma
Read this article at
Abstract
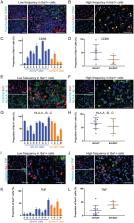
Microglia and macrophages are the largest component of the inflammatory infiltrate in glioblastoma (GBM). However, whether there are differences in their representation and activity in the prognostically-favorable isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)-mutated compared to -wild type GBMs is unknown. Studies on human specimens of untreated IDH-mutant GBMs are rare given they comprise 10% of all GBMs and often present at lower grades, receiving treatments prior to dedifferentiation that can drastically alter microglia and macrophage phenotypes. We were able to obtain large samples of four previously untreated IDH-mutant GBM. Using flow cytometry, immunofluorescence techniques with automated segmentation protocols that quantify at the individual-cell level, and comparison between single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) databases of human GBM, we discerned dissimilarities between GBM-associated microglia and macrophages (GAMMs) in IDH-mutant and -wild type GBMs. We found there are significantly fewer GAMM in IDH-mutant GBMs, but they are more pro-inflammatory, suggesting this contributes to the better prognosis of these tumors. Our pro-inflammatory score which combines the expression of inflammatory markers (CD68/HLA-A, -B, -C/TNF/CD163/IL10/TGFB2), Iba1 intensity, and GAMM surface area also indicates that more pro-inflammatory GAMMs are associated with longer overall survival independent of IDH status. Interrogation of scRNA-seq databases demonstrates microglia in IDH-mutants are mainly pro-inflammatory, while anti-inflammatory macrophages that upregulate genes such as FCER1G and TYROBP predominate in IDH-wild type GBM. Taken together, these observations are the first head-to-head comparison of GAMMs in treatment-naïve IDH-mutant versus -wild type GBMs. Our findings highlight biological disparities in the innate immune microenvironment related to IDH prognosis that can be exploited for therapeutic purposes.
Related collections
Most cited references33

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A step-by-step workflow for low-level analysis of single-cell RNA-seq data with Bioconductor
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Diverse Requirements for Microglial Survival, Specification, and Function Revealed by Defined-Medium Cultures.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found