- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Biological relevance and therapeutic potential of G-quadruplex structures in the human noncoding transcriptome
Read this article at
Abstract
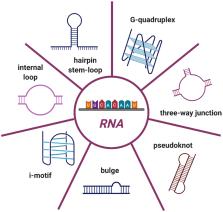
Noncoding RNAs are functional transcripts that are not translated into proteins. They represent the largest portion of the human transcriptome and have been shown to regulate gene expression networks in both physiological and pathological cell conditions. Research in this field has made remarkable progress in the comprehension of how aberrations in noncoding RNA drive relevant disease-associated phenotypes; however, the biological role and mechanism of action of several noncoding RNAs still need full understanding. Besides fulfilling its function through sequence-based mechanisms, RNA can form complex secondary and tertiary structures which allow non-canonical interactions with proteins and/or other nucleic acids. In this context, the presence of G-quadruplexes in microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs is increasingly being reported. This evidence suggests a role for RNA G-quadruplexes in controlling microRNA biogenesis and mediating noncoding RNA interaction with biological partners, thus ultimately regulating gene expression. Here, we review the state of the art of G-quadruplexes in the noncoding transcriptome, with their structural and functional characterization. In light of the existence and further possible development of G-quadruplex binders that modulate G-quadruplex conformation and protein interactions, we also discuss the therapeutic potential of G-quadruplexes as targets to interfere with disease-associated noncoding RNAs.
Related collections
Most cited references195
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found