- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
ST218 Klebsiella pneumoniae became a high-risk clone for multidrug resistance and hypervirulence
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The occurrence of multidrug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (MDR-hvKp) worldwide poses a great challenge for public health. Few studies have focused on ST218 MDR-hvKp.
Methods
Retrospective genomic surveillance was conducted at the Peking University Third Hospital from 2017 and clinical information was obtained. To understand genomic and microbiological characteristics, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, plasmid conjugation and stability, biofilm formation, serum killing, growth curves and whole-genome sequencing were performed. We also assessed the clinical and microbiological characteristics of ST218 compared with ST23.
Results
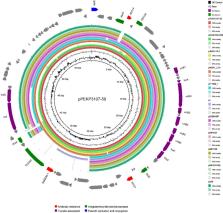
A total of eleven ST218 Kp isolates were included. The most common infection type was lower respiratory tract infection (72.7%, 8/11) in our hospital, whereas ST23 hvKp (72.7%, 8/11) was closely associated with bloodstream infection. Notably, nosocomial infections caused by ST218 (54.5%, 6/11) was slightly higher than ST23 (36.4%, 4/11). All of the ST218 and ST23 strains presented with the virulence genes combination of iucA + iroB + peg344 + rmpA + rmpA2. Interestingly, the virulence score of ST218 was lower than ST23, whereas one ST218 strain (pPEKP3107) exhibited resistance to carbapenems, cephalosporins, β-lactamase/inhibitors and quinolones and harbored an ~ 59-kb IncN type MDR plasmid carrying resistance genes including bla NDM-1, dfrA14 and qnrS1. Importantly, bla NDM-1 and qnrS1 were flanked with IS 26 located within the plasmid that could successfully transfer into E. coli J53. Additionally, PEKP2044 harbored an ~ 41-kb resistance plasmid located within tetA indicating resistance to doxycycline.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found