- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Norovirus genotype distribution in outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis among children and older people: an 8-year study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Noroviruses (NoVs) are the most frequent cause of acute gastroenteritis worldwide among people of all ages and the leading cause of gastrointestinal disease outbreaks in various settings. To clarify the differences in epidemic situations among different settings, we investigated epidemiological trends and the distribution of NoV genotypes in Yokohama, Japan.
Methods
Between September 2007 and August 2015, 746 outbreaks of NoV gastroenteritis were reported in kindergarten/nursery schools (K/Ns), primary schools (PSs), and nursing homes for the aged (NHs). Stool samples were collected for NoV testing, and the NoV gene was amplified and sequenced to determine the genotype.
Results
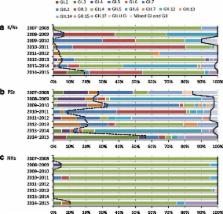
During the eight seasons, 248 NoV outbreaks occurred in K/Ns, 274 outbreaks in PSs, and 224 outbreaks in NHs. These outbreaks occurred throughout the year, except in August, and the number increased in November and peaked in December. The number of outbreaks that occurred from November to February comprised 76.8 % of all outbreaks. The outbreaks originated in K/Ns or PSs in every season, except for one season. Five genogroup (G)I and nine GII genotypes in K/Ns, six GI and 10 GII genotypes in PSs, and three GI and six GII genotypes in NHs were detected during the eight seasons. GII.4 was the most prevalent genotype in K/Ns and NHs. However, GII.6 was the most prevalent genotype in PSs. The epidemic genotypes in K/Ns and PSs changed by NoV season, although GII.4 was always predominant in NHs. Moreover, the distribution of genotypes was significantly different between epidemic and non-epidemic periods in each facility ( p < 0.01 for all).
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Norovirus gastroenteritis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Norovirus illness is a global problem: emergence and spread of norovirus GII.4 variants, 2001-2007.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found