- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
miR-500a-3p promotes cancer stem cells properties via STAT3 pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
miR-500a-3p has been demonstrated to be involved in the development, progression and metastasis in several human cancers. Constitutive activation of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway has been reported to play an important role in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).The purpose of this study was to determine the biological roles and clinical significance of miR-500a-3p in HCC and to identify whether miR-500a-3p has an effect on the activity of JAK/STAT3 signaling in HCC.
Methods
miR-500a-3p expression was examined by real-time PCR in 8 paired HCC tissues and individual 120 HCC tissues respectively. Statistical analysis was performed to explore the clinical correlation between miR-500a-3p expression and clinicopathological features and overall and relapse-free survival in HCC patients. In vitro and in vivo assays were performed to investigate the biological roles of miR-500a-3p in HCC. The bioinformatics analysis, real-time PCR, western blot and luciferase reporter assay were performed to discern and examine the relationship between miR-500a-3p and its potential targets. Clinical correlation of miR-500a-3p with its targets was examined in HCC tissues.
Results
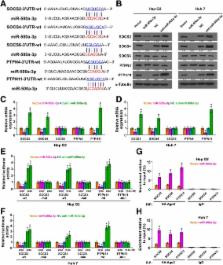
miR-500a-3p is dramatically elevated in HCC tissues and cells and high expression of miR-500a-3p correlates with poor overall and relapse-free survival in HCC patients. Upregulating miR-500a-3p enhances, while silencing miR-500a-3p suppresses, the spheroid formation ability, fraction of side population and expression of cancer stem cell factors in vitro and tumorigenicity in vivo in HCC cells. Our findings further reveal miR-500a-3p promotes the cancer stem cell characteristics via targeting multiple negative regulators of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway, including SOCS2, SOCS4 and PTPN11, leading to constitutive activation of STAT3 signaling. Moreover, the inhibitory effects of anti-miR-500a-3p on cancer stem cell phenotypes and activity of STAT3 signaling were reversed by silencing SOCS2, SOCS4 and PTPN11 in miR-500a-3p-downexpressing cells, respectively. Clinical correlation of miR-500a-3p with the targets was examined in human HCC tissues.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is required for growth of CD44⁺CD24⁻ stem cell-like breast cancer cells in human tumors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found