- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Reaction-dependent optical behavior and theoretical perspectives of colloidal ZnSe quantum dots
Read this article at
Abstract
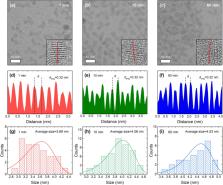
Colloidal quantum dots (QDs) are attracting research interest because of their unique optical properties that result from the quantum confinement effect. ZnSe QDs, which are II–VI semiconductors, offer a wide direct bandgap (2.7 eV), making them promising for applications such as light-emitting diodes, photodetectors, and biomedical labeling. In the present work, colloidal ZnSe (QDs) were synthesized by the hot-injection method with a Zn:Se ratio of 1:1. The optical properties of ZnSe QDs obtained at different reaction times were investigated by spectrophotometric UV–vis absorption and emission measurements. The as-synthesized ZnSe QDs exhibit blue excitonic emission, and no defect emission was detected. Transmission electron micrographs indicated that the QDs have a spherical morphology with dimensions ranging from 3.69 to 4.53 nm. In particular, the Brus model was applied to demonstrate a correlation between the QD sizes and the optical bandgaps obtained from Tauc plots.
Related collections
Most cited references46
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Band-edge exciton in quantum dots of semiconductors with a degenerate valence band: Dark and bright exciton states
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found