- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
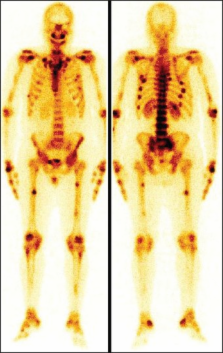
Bone scintigraphic patterns in patients of tumor induced osteomalacia
Read this article at
Abstract
Tumor induced osteomalacia (TIO) or oncogenic osteomalacia is a rare condition associated with small tumor that secretes one of the phosphaturic hormones, i.e., fibroblast growth factor 23, resulting in abnormal phosphate metabolism. Patients may present with non-specific symptoms leading to delay in the diagnosis. Extensive skeletal involvement is frequently seen due to delay in the diagnosis and treatment. The small sized tumor and unexpected location make the identification of tumor difficult even after diagnosis of osteogenic osteomalacia. The bone scan done for the skeletal involvement may show the presence of metabolic features and the scan findings are a sensitive indicator of metabolic bone disorders. We present the bone scan findings in three patients diagnosed to have TIO.
Related collections
Most cited references20
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Tumor-induced osteomalacia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found