- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Pure Tethered Cervical Cord and Review of Literature
Read this article at
Abstract
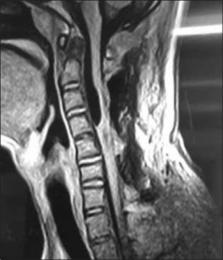
Tethering of the spinal cord in the lumbosacral region with myelomeningocele is a well-known phenomenon. Only sporadic cases of tethering along the rest of the neuraxis, including the hindbrain, cervical, and thoracic spinal cord have been documented, always along with some associated congenital malformations (hydrocephalus, Chiari malformation, myelomeningocele, meningocele, hamartomatous stalk, spina bifida occulta, intramedullary lipoma, intradural fibrous adhesions, the fusion of the sixth and seventh cervical vertebrae, split cord malformation, or low-lying cord). In this report, 14-year-old male developed symptoms related to tethering of the cervical spinal cord, but without any associated congenital malformations, that is the pure tethered cervical cord. This causes his moribund status and makes the manuscript unique and contributes to the hitherto literature. The authors discuss the diagnosis, treatment, and postoperative course of this entity. The uniqueness in treatment is that we have operated the case without the help of intraoperative somatosensory evoked potentials and motor evoked potential from posterolateral approach under local anesthesia.
Related collections
Most cited references13
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cervical myelomeningoceles.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Split cervical spinal cord malformation and vertebral dysgenesis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found