- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Plant–microbe interactions ameliorate phosphate-mediated responses in the rhizosphere: a review
Read this article at
Abstract
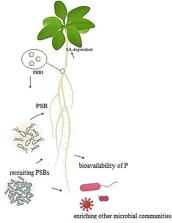
Phosphorus (P) is one of the essential minerals for many biochemical and physiological responses in all biota, especially in plants. P deficiency negatively affects plant performance such as root growth and metabolism and plant yield. Mutualistic interactions with the rhizosphere microbiome can assist plants in accessing the available P in soil and its uptake. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of plant–microbe interactions that facilitate P uptake by the plant. We focus on the role of soil biodiversity in improved P uptake by the plant, especially under drought conditions. P-dependent responses are regulated by phosphate starvation response (PSR). PSR not only modulates the plant responses to P deficiency in abiotic stresses but also activates valuable soil microbes which provide accessible P. The drought-tolerant P-solubilizing bacteria are appropriate for P mobilization, which would be an eco-friendly manner to promote plant growth and tolerance, especially in extreme environments. This review summarizes plant–microbe interactions that improve P uptake by the plant and brings important insights into the ways to improve P cycling in arid and semi-arid ecosystems.
Related collections
Most cited references61
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Eutrophication science: where do we go from here?
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mycorrhizas and soil structure.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found