- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Interventions to decrease skin cancer risk in outdoor workers: update to a 2007 systematic review
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Outdoor workers are at high risk of harmful ultraviolet radiation exposure and are identified as an at risk group for the development of skin cancer. This systematic evidence based review provides an update to a previous review published in 2007 about interventions for the prevention of skin cancer in outdoor workers.
Results
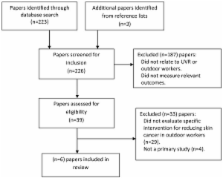
This review includes interventions published between 2007-2012 and presents findings about sun protection behaviours and/or objective measures of skin cancer risk. Six papers met inclusion criteria and were included in the review. Large studies with extended follow-up times demonstrated the efficacy of educational and multi-component interventions to increase sun protection, with some higher use of personal protective equipment such as sunscreen. However, there is less evidence for the effectiveness of policy or specific intervention components.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Meta-analysis of risk factors for cutaneous melanoma: II. Sun exposure.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Extending an evidence hierarchy to include topics other than treatment: revising the Australian 'levels of evidence'
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found