- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Progress in the functional modification of graphene/graphene oxide: a review
Read this article at
Abstract
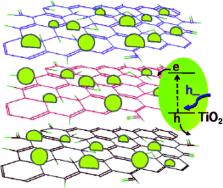
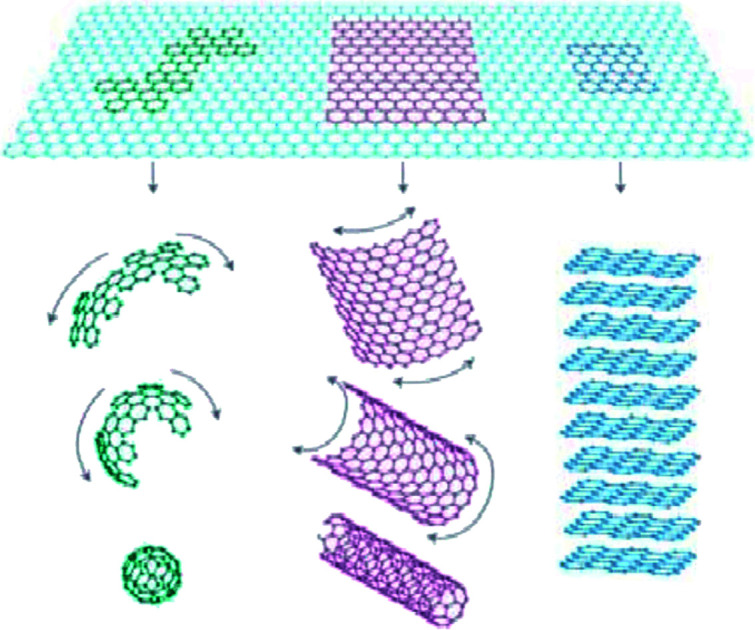
Graphene and graphene oxide have attracted tremendous interest over the past decade due to their unique and excellent electronic, optical, mechanical, and chemical properties. This review focuses on the functional modification of graphene and graphene oxide. First, the basic structure, preparation methods and properties of graphene and graphene oxide are briefly described. Subsequently, the methods for the reduction of graphene oxide are introduced. Next, the functionalization of graphene and graphene oxide is mainly divided into covalent binding modification, non-covalent binding modification and elemental doping. Then, the properties and application prospects of the modified products are summarized. Finally, the current challenges and future research directions are presented in terms of surface functional modification for graphene and graphene oxide.
Abstract
Graphene and graphene oxide have attracted tremendous interest over the past decade due to their unique and excellent electronic, optical, mechanical, and chemical properties.
Related collections
Most cited references97
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Preparation of Graphitic Oxide
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found