- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Dietary fatty acid metabolism of brown adipose tissue in cold-acclimated men
Read this article at
Abstract
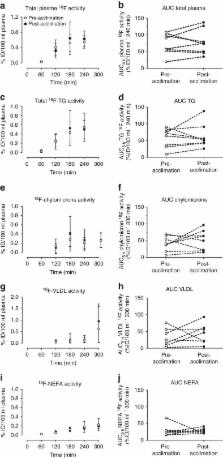
In rodents, brown adipose tissue (BAT) plays an important role in producing heat to defend against the cold and can metabolize large amounts of dietary fatty acids (DFA). The role of BAT in DFA metabolism in humans is unknown. Here we show that mild cold stimulation (18 °C) results in a significantly greater fractional DFA extraction by BAT relative to skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue in non-cold-acclimated men given a standard liquid meal containing the long-chain fatty acid PET tracer, 14( R, S)-[ 18F]-fluoro-6-thia-heptadecanoic acid ( 18FTHA). However, the net contribution of BAT to systemic DFA clearance is comparatively small. Despite a 4-week cold acclimation increasing BAT oxidative metabolism 2.6-fold, BAT DFA uptake does not increase further. These findings show that cold-stimulated BAT can contribute to the clearance of DFA from circulation but its contribution is not as significant as the heart, liver, skeletal muscles or white adipose tissues.
Abstract
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) takes up and burns fatty acids for thermogenesis in mice. Here the authors use PET to show that, in humans, cold stimulation increases BAT dietary fatty acid uptake from plasma and oxidative metabolism, although, unlike mice, human BAT takes up less fatty acids than other metabolic tissues.
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Brown adipose tissue oxidative metabolism contributes to energy expenditure during acute cold exposure in humans.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Different metabolic responses of human brown adipose tissue to activation by cold and insulin.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found