- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Modes of TAL effector-mediated repression
Read this article at
Abstract
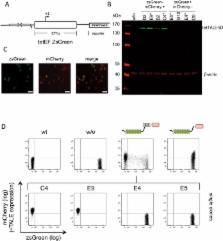
Engineered transcription activator-like effectors, or TALEs, have emerged as a new class of designer DNA-binding proteins. Their DNA recognition sites can be specified with great flexibility. When fused to appropriate transcriptional regulatory domains, they can serve as designer transcription factors, modulating the activity of targeted promoters. We created tet operator ( tetO)-specific TALEs (tetTALEs), with an identical DNA-binding site as the Tet repressor (TetR) and the TetR-based transcription factors that are extensively used in eukaryotic transcriptional control systems. Different constellations of tetTALEs and tetO modified chromosomal transcription units were analyzed for their efficacy in mammalian cells. We find that tetTALE-silencers can entirely abrogate expression from the strong human EF1α promoter when binding upstream of the transcriptional control sequence. Remarkably, the DNA-binding domain of tetTALE alone can effectively counteract trans-activation mediated by the potent tet trans-activator and also directly interfere with RNA polymerase II transcription initiation from the strong CMV promoter. Our results demonstrate that TALEs can act as highly versatile tools in genetic engineering, serving as trans-activators, trans-silencers and also competitive repressors.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Transcription factors: from enhancer binding to developmental control.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found