- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Two Toxic Lipid Aldehydes, 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (4-HHE) and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), Accumulate in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Read this article at
Abstract
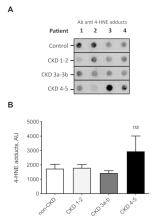
Lipid aldehydes originating from the peroxidation of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids are increased in hemodialysis (HD) patients, a process already known to promote oxidative stress. However, data are lacking for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) before the initiation of HD. We prospectively evaluated the changes of plasma concentrations of two major lipid aldehydes, 4-HHE and 4-HNE, according to the decrease of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in 40 CKD and 13 non-CKD participants. GFR was measured by inulin or iohexol clearance. Thus, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE) and 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (4-HHE) were quantitated in plasma by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry and their covalent adducts on proteins were quantified by immunoblotting. On the one hand, 4-HHE plasma concentration increased from CKD stage I–II to CKD stage IV–V compared to non-CKD patients (4.5-fold higher in CKD IV–V, p < 0.005). On the other hand, 4-HNE concentration only increased in CKD stage IV–V patients (6.2-fold, p < 0.005). The amount of covalent adducts of 4-HHE on plasma protein was 9.5-fold higher in CKD patients than in controls ( p < 0.005), while no difference was observed for 4-HNE protein adducts. Plasma concentrations of 4-HNE and 4-HHE are increased in CKD IV–V patients before the initiation of hemodialysis.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Normal and pathologic concentrations of uremic toxins.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oxidative stress and inflammation, a link between chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found