- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Machine learning-based analysis of a semi-automated PI-RADS v2.1 scoring for prostate cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System version 2.1 (PI-RADS v2.1) was developed to standardize the interpretation of multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) for prostate cancer (PCa) detection. However, a significant inter-reader variability among radiologists has been found in the PI-RADS assessment. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of an in-house developed semi-automated model for PI-RADS v2.1 scoring using machine learning methods.
Methods
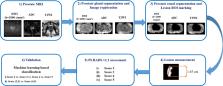
The study cohort included an MRI dataset of 59 patients (PI-RADS v2.1 score 2 = 18, score 3 = 10, score 4 = 16, and score 5 = 15). The proposed semi-automated model involved prostate gland and zonal segmentation, 3D co-registration, lesion region of interest marking, and lesion measurement. PI-RADS v2.1 scores were assessed based on lesion measurements and compared with the radiologist PI-RADS assessment. Machine learning methods were used to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the proposed model by classification of PI-RADS v2.1 scores.
Results
The semi-automated PI-RADS assessment based on the proposed model correctly classified 50 out of 59 patients and showed a significant correlation ( r = 0.94, p < 0.05) with the radiologist assessment. The proposed model achieved an accuracy of 88.00% ± 0.98% and an area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.94 for score 2 vs. score 3 vs. score 4 vs. score 5 classification and accuracy of 93.20 ± 2.10% and AUC of 0.99 for low score vs. high score classification using fivefold cross-validation.
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found