- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Towards Improving the Efficacy of PSMA-Targeting Radionuclide Therapy for Late-Stage Prostate Cancer—Combination Strategies
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose of Review
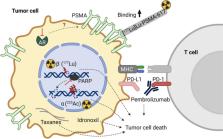
[ 177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 is a radiopharmaceutical that emits beta-minus radiation and targets prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-positive prostate cancer. Despite its clinical success, there are still patients not showing sufficient response rates. This review compiles latest studies aiming at therapy improvement in [ 177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617-naïve and -resistant patients by alternative or combination treatments.
Recent Findings
A variety of agents to combine with [ 177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 are currently under investigation including alpha radiation-emitting pharmaceuticals, radiosensitizers, taxane chemotherapeutics, androgen receptor pathway inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and external beam radiation. Actinium-225 ( 225Ac)-labeled PSMA-targeting inhibitors are the most studied pharmaceuticals for combination therapy or as an alternative for treatment after progression under [ 177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 therapy.
Summary
Alpha emitters seem to have a potential of achieving a response to PSMA-targeting radionuclide therapy in both initial non-responders or responders to [ 177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 later developing treatment resistance. Emerging evidence for immunostimulatory effects of radiopharmaceuticals and first prospective studies support the combination of [ 177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and immune checkpoint inhibition for late-stage prostate cancer.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Lutetium-177–PSMA-617 for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
[177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 versus cabazitaxel in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (TheraP): a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found