- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The risk and trend of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis in rheumatoid arthritis: a general population-based study
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives
To estimate the overall risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) among patients newly diagnosed with RA compared with the general population without RA; and to estimate the risk trends of VTE, PE and DVT after RA diagnosis up to 5 years compared with the general population.
Methods
Using previously validated RA case definition, we conducted a matched cohort study using the population-based administrative health database from the province of British Columbia, Canada. We calculated incidence rates (IRs) and fully adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for the risk of VTE, DVT and PE after RA index date.
Results
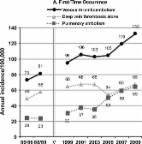
Among 39 142 incident RA patients (66% female, mean age 60), 1432, 543 and 1068 developed VTE, PE and DVT, respectively. IRs for the RA cohort were 3.79, 1.43 and 2.82 per 1000 person-years vs 2.70, 1.03 and 1.94 per 1000 person-years for the non-RA cohort. After adjusting for VTE risk factors, the HRs (95% CI) were 1.28 (1.20, 1.36), 1.25 (1.13, 1.39) and 1.30 (1.21, 1.40) for VTE, PE and DVT, respectively. The fully adjusted HRs for VTE during the first five years after RA diagnosis were 1.60, 1.47, 1.40, 1.30 and 1.28, respectively. A similar trend was shown in PE.
Conclusion
This population-based study demonstrates that RA patients have an increased risk of VTE, PE and DVT after diagnosis compared with the general population. This risk is independent of traditional VTE risk factors and is highest during the first year after RA diagnosis, then progressively declined.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
