- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical evaluation of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for detecting pathogens in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid collected from children with community-acquired pneumonia
Read this article at
Abstract
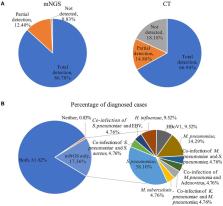
This study is to evaluate the usefulness of pathogen detection using metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) specimens from children with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). We retrospectively collected BALF specimens from 121 children with CAP at Tianjin Children's Hospital from February 2021 to December 2021. The diagnostic performances of mNGS and conventional tests (CT) (culture and targeted polymerase chain reaction tests) were compared, using composite diagnosis as the reference standard. The results of mNGS and CT were compared based on pathogenic and non-pathogenic organisms. Pathogen profiles and co-infections between the mild CAP and severe CAP groups were also analyzed. The overall positive coincidence rate was 86.78% (105/121) for mNGS and 66.94% (81/121) for CT. The proportion of patients diagnosed using mNGS plus CT increased to 99.18%. Among the patients, 17.36% were confirmed only by mNGS; Streptococcus pneumoniae accounted for 52.38% and 23.8% of the patients were co-infected. Moreover, Bordetella pertussis and Human bocavirus (HBoV) were detected only using mNGS. Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which was identified in 89 (73.55%) of 121 children with CAP, was the most frequent pathogen detected using mNGS. The infection rate of M. pneumoniae in the severe CAP group was significantly higher than that in the mild CAP group ( P = 0.007). The symptoms of single bacterial infections (except for mycoplasma) were milder than those of mycoplasma infections. mNGS identified more bacterial infections when compared to the CT methods and was able to identify co-infections which were initially missed on CT. Additionally, it was able to identify pathogens that were beyond the scope of the CT methods. The mNGS method is a powerful supplement to clinical diagnostic tools in respiratory infections, as it can increase the precision of diagnosis and guide the use of antibiotics.
Related collections
Most cited references39

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found