- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
CoCiter: An Efficient Tool to Infer Gene Function by Assessing the Significance of Literature Co-Citation
Read this article at
Abstract
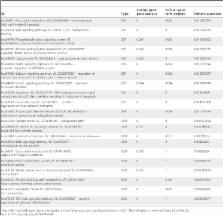
A routine approach to inferring functions for a gene set is by using function enrichment analysis based on GO, KEGG or other curated terms and pathways. However, such analysis requires the existence of overlapping genes between the query gene set and those annotated by GO/KEGG. Furthermore, GO/KEGG databases only maintain a very restricted vocabulary. Here, we have developed a tool called “CoCiter” based on literature co-citations to address the limitations in conventional function enrichment analysis. Co-citation analysis is widely used in ranking articles and predicting protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Our algorithm can further assess the co-citation significance of a gene set with any other user-defined gene sets, or with free terms. We show that compared with the traditional approaches, CoCiter is a more accurate and flexible function enrichment analysis method. CoCiter is freely available at www.picb.ac.cn/hanlab/cociter/.
Related collections
Most cited references16
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ontological analysis of gene expression data: current tools, limitations, and open problems.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found