- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Aberrant LncRNA Expression in Leukemia
Read this article at
Abstract
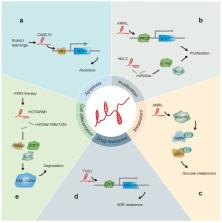
Leukemia is a common malignant cancer of the hematopoietic system, whose pathogenesis has not been fully elucidated. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides without protein-coding function. Recent studies report their role in cellular processes such as the regulation of gene expression, as well as in the carcinogenesis, occurrence, development, and prognosis of various tumors. Evidence indicating relationships between a variety of lncRNAs and leukemia pathophysiology has increased dramatically in the previous decade, with specific lncRNAs expected to serve as diagnostic biomarkers, novel therapeutic targets, and predictors of clinical outcomes. Furthermore, these lncRNAs might offer insight into disease pathogenesis and novel treatment options. This review summarizes progress in studies on the role(s) of lncRNAs in leukemia.
Related collections
Most cited references105
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Long non-coding RNA ANRIL is required for the PRC2 recruitment to and silencing of p15(INK4B) tumor suppressor gene.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found