- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Defunctioning stoma before neoadjuvant treatment or resection of endoscopically obstructing rectal cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
Aim
To investigate whether patients with endoscopically untraversable rectal cancer may benefit from a defunctioning stoma created before neoadjuvant therapy or resectional surgery.
Methods
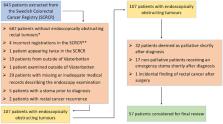
This retrospective study comprise patients diagnosed with rectal cancer during 2007–2020 in Region Västerbotten, Sweden. The primary outcome was time between diagnosis and any treatment, while survival and the incidence of complications were secondary outcomes. Excluded were patients without endoscopic obstruction, patients already having a stoma, patients with recurrent disease, palliative patients, and patients receiving a stoma shortly after diagnosis due to any urgent bowel-related complication. Data were obtained from the Swedish Colorectal Cancer Registry and medical records. Kaplan–Meier failure curves were drawn, and a multivariable Cox regression model was employed for confounding adjustment.
Results
Out of 843 patients, 57 remained after applying exclusion criteria. Some 12/57 (21%) patients received a planned stoma before treatment, and the remainder received upfront neoadjuvant therapy or surgery. Median time to any treatment was 51 days for the planned stoma group and 36 days for the control group, with an adjusted hazard ratio of 0.28 (95% confidence interval: 0.12–0.64). Complications occurred at a rate of 5/12 (42%) and 7/45 (16%) in the planned stoma group and control group, respectively. Survival was similar between groups.
Conclusion
A planned stoma results in treatment delay, but it remains unclear whether this is clinically relevant. Complications were more common in the planned stoma group, although the data are limited. While larger studies are needed, it seems feasible to avoid defunctioning stomas even in endoscopically obstructing rectal cancers.
Related collections
Most cited references8
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Extended Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Japan Clinical Oncology Group postoperative complications criteria
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Statistics review 12: Survival analysis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found