- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trends in incidence, health care consumption, and costs for proximal femoral fractures in the Netherlands between 2000 and 2019: a nationwide study
Read this article at
Abstract
Summary
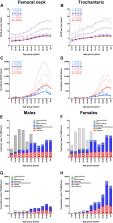
This study evaluated the incidence rates and societal burden of hip fractures in The Netherlands. Although incidence in the elderly population is decreasing and hospital stay is at an all-time low, the burden of medical costs and crude numbers of proximal femoral fractures are still rising in our aging population.
Purpose
The aim of this nationwide study was to provide an overview of the incidence rate and economic burden of acute femoral neck and trochanteric fractures in The Netherlands.
Methods
Data of patients who sustained acute proximal femoral fractures in the period January 1, 2000, to December 31, 2019, were extracted from the National Medical Registration of the Dutch Hospital Database. The incidence rate, hospital length of stay (HLOS), health care and lost productivity costs, and years lived with disability (YLD) were calculated for age- and sex-specific groups.
Results
A total of 357,073 patients were included. The overall incidence rate increased by 22% over the 20-year study period from 16.4 to 27.1/100,000 person-years (py). The age-specific incidence rate in elderly > 65 years decreased by 16% (from 649.1 to 547.6/100,000 py). The incidence rate in men aged > 90 has surpassed the incidence rate in women. HLOS decreased in all age groups, hip fracture subtypes, and sexes from a mean of 18.5 to 7.2 days. The mean health care costs, over the 2015–2019 period, were lower for men (€17,723) than for women (€23,351) and increased with age to €26,639 in women aged > 80. Annual cumulative costs reached €425M, of which 73% was spent on women.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Hip fractures in the elderly: a world-wide projection.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The friction cost method for measuring indirect costs of disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found