- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Synthesis and properties of porous CLEAs lipase by the calcium carbonate template method and its application in biodiesel production

Read this article at
Abstract
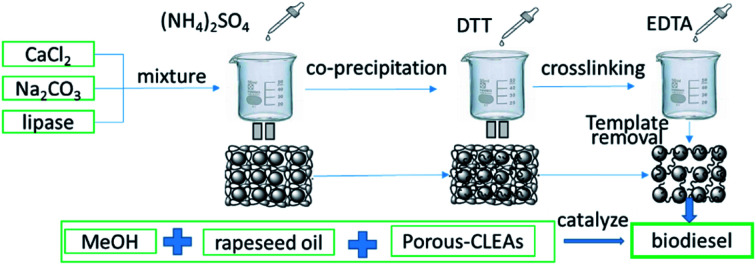
In this work, porous cross-linked enzyme aggregates (p-CLEAs) were synthesized by the in situ co-precipitation method using CaCO 3 microparticles as templates. The preparation procedure involved the immobilization of crude lipase as CLEAs via precipitation with ammonium sulfate and entrapping these lipase molecules into the CaCO 3 templates, followed by DTT (dithiothreitol)-induced assembly of lipase molecules to form lipase microparticles (lipase molecules were assembled into microparticles internally using disulfide bonds within the lipase molecules as the molecular linkers and stimulated by dithiothreitol); finally, the removal of CaCO 3 templates was performed by EDTA to form pores in CLEAs. The scanning electron microscopy analysis of p-CLEAs showed a porous structure. p-CLEAs showed obvious improvement in thermal stability (after incubation at 65 °C, p-CLEAs lipase retained 86% relative activity, while free lipase retained only 33.67%) and pH stability (p-CLEAs relative activity was over 90% while for free lipase, the relative activity ranged from 72% to 89% from pH 6 to 9) than free lipase and could hold relatively high activity retention without activity loss at 4 °C for more than six months. The application of p-CLEAs in producing biodiesel showed a higher degree of conversion. The conversion of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) was 89.7%; this value was higher by approximately 7.4% compared to that of the conventional CLEAs under the optimized conditions of a methanol–oil molar ratio of 6 : 1, with a p-CLEAs lipase dose of 20% and water content of 3% at 45 °C for 24 h. The FAME conversion remained greater than 70% even after reusing the p-CLEAs lipase for 8 reactions. The results demonstrated that the p-CLEAs lipase is suitable for applications in the preparation of biodiesel.
Abstract
Porous cross-linked enzyme aggregates (p-CLEAs) were synthesized. This p-CLEAs presented a complete structure with abundant channels, large specific surface and more efficient catalytic effect compared with conventional CLEAs.
Related collections
Most cited references28
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Enzyme Immobilization: An Overview on Methods, Support Material, and Applications of Immobilized Enzymes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Parameters in preparation and characterization of cross linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs)
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found