- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sex hormone-binding globulin and arthritis: a Mendelian randomization study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) has been reported to be a risk factor associated with the development of arthritis by previous observational studies more so of three common forms of arthritis: osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and ankylosing spondylitis (AS). This study aimed to determine whether the concentrations of circulating SHBG are causally associated with the risk of OA, RA, and AS.
Methods
The two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) approach was used for this study. The inverse-variance-weighted (IVW) method was used for the main analysis. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with SHBG were selected from a large genome-wide association study (GWAS) of 28,837 European individuals. The summary statistics for OA, RA, and AS were extracted from the UK Biobank Resource ( n = 361,141) and a GWAS dataset ( n = 455,221).
Results
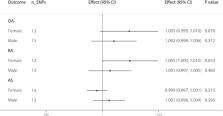
Positive causal associations were found between circulating SHBG concentrations and OA (effect = 1.086; 95% CI, 1.009 to 1.168; P = 0.027) and RA (effect = 1.003; 95% CI, 1.000 to 1.007; P = 0.047) in overall analyses. However, there was no evidence of association between SHBG levels and AS. Based on the stratification of skeletal sites, SHBG levels were found to be significantly associated with hip OA (effect = 1.423; 95% CI, 1.219 to 1.660; P = 7.753 × 10 −6). However, this was not the case with knee OA.
Conclusions
There were positive causal effects of circulating SHBG on the development of OA and RA. Moreover, there was a site-specific association between SHBG and hip OA. Evidently, measurement of SHBG in serum could be valuable in the clinical assessment of arthritis especially in early screening and prevention of OA and RA. However, the mechanisms by which SHBG plays causal roles in the development of arthritis require further investigations.
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Mendelian Randomization.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found