- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Development and Validation of Prediction Models for Severe Complications After Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Study Based on the Stroke Registry of Northwestern Germany
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The treatment of stroke has been undergoing rapid changes. As treatment options progress, prediction of those under risk for complications becomes more important. Available models have, however, frequently been built based on data no longer representative of today’s care, in particular with respect to acute stroke management. Our aim was to build and validate prediction models for 4 clinically important, severe outcomes after stroke.
Methods and Results
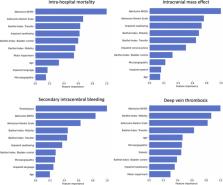
We used German registry data from 152 710 patients with acute ischemic stroke obtained in 2016 (development) and 2017 (validation). We took into account potential predictors that were available at admission and focused on in‐hospital mortality, intracranial mass effect, secondary intracerebral hemorrhage, and deep vein thrombosis as outcomes. Validation cohort prediction and calibration performances were assessed using the following 4 statistical approaches: logistic regression with backward selection, l1‐regularized logistic regression, k‐nearest neighbor, and gradient boosting classifier. In‐hospital mortality and intracranial mass effects could be predicted with high accuracy (both areas under the curve, 0.90 [95% CI, 0.90–0.90]), whereas the areas under the curve for intracerebral hemorrhage (0.80 [95% CI, 0.80–0.80]) and deep vein thrombosis (0.73 [95% CI, 0.73–0.73]) were considerably lower. Stroke severity was the overall most important predictor. Models based on gradient boosting achieved better performances than those based on logistic regression for all outcomes. However, area under the curve estimates differed by a maximum of 0.02.
Conclusions
We validated prediction models for 4 severe outcomes after acute ischemic stroke based on routinely collected, recent clinical data. Model performance was superior to previously proposed approaches. These predictions may help to identify patients at risk early after stroke and thus facilitate an individualized level of care.
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A systematic review shows no performance benefit of machine learning over logistic regression for clinical prediction models
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.