- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Risk Factors Amenable to Primary Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Among Disaggregated Racial and Ethnic Subgroups in the U.S.
Read this article at
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Race and ethnicity data disaggregated into detailed subgroups may reveal pronounced heterogeneity in diabetes risk factors. We therefore used disaggregated data to examine the prevalence of type 2 diabetes risk factors related to lifestyle behaviors and barriers to preventive care among adults in the U.S.
RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS
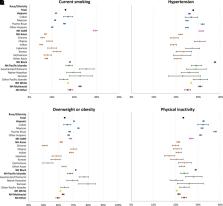
We conducted a pooled cross-sectional study of 3,437,640 adults aged ≥18 years in the U.S. without diagnosed diabetes from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (2013–2021). For self-reported race and ethnicity, the following categories were included: Hispanic (Cuban, Mexican, Puerto Rican, Other Hispanic), non-Hispanic (NH) American Indian/Alaska Native, NH Asian (Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese, Other Asian), NH Black, NH Pacific Islander (Guamanian/Chamorro, Native Hawaiian, Samoan, Other Pacific Islander), NH White, NH Multiracial, NH Other. Risk factors included current smoking, hypertension, overweight or obesity, physical inactivity, being uninsured, not having a primary care doctor, health care cost concerns, and no physical exam in the past 12 months.
RESULTS
Prevalence of hypertension, lifestyle factors, and barriers to preventive care showed substantial heterogeneity among both aggregated, self-identified racial and ethnic groups and disaggregated subgroups. For example, the prevalence of overweight or obesity ranged from 50.8% (95% CI 49.1–52.5) among Chinese adults to 79.8% (73.5–84.9) among Samoan adults. Prevalence of being uninsured among Hispanic subgroups ranged from 11.4% (10.9–11.9) among Puerto Rican adults to 33.0% (32.5–33.5) among Mexican adults.
Graphical Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found

